More and more research on how cannabis effects the human body appears every year. Let’s have a look at the most interesting scientifically proven aspects of cannabis consumption, that include both positive and negative effects.
Mostly, these effects depend on proportion of active substances of cannabis as well as methods and dosage of its usage. Marijuana contains approximately 60 pharmacologically active compounds. Two most important of them are CBD and THC.
How does CBD effect on the human body?
CBD (cannabidiol) is one of the most important non-psychoactive components of cannabis. According to the latest medical research it has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and relaxing properties. These effects are mostly achieved by CBD slowing down the main vital processes in a human body – starting from the heartbeat ending with the cell division.
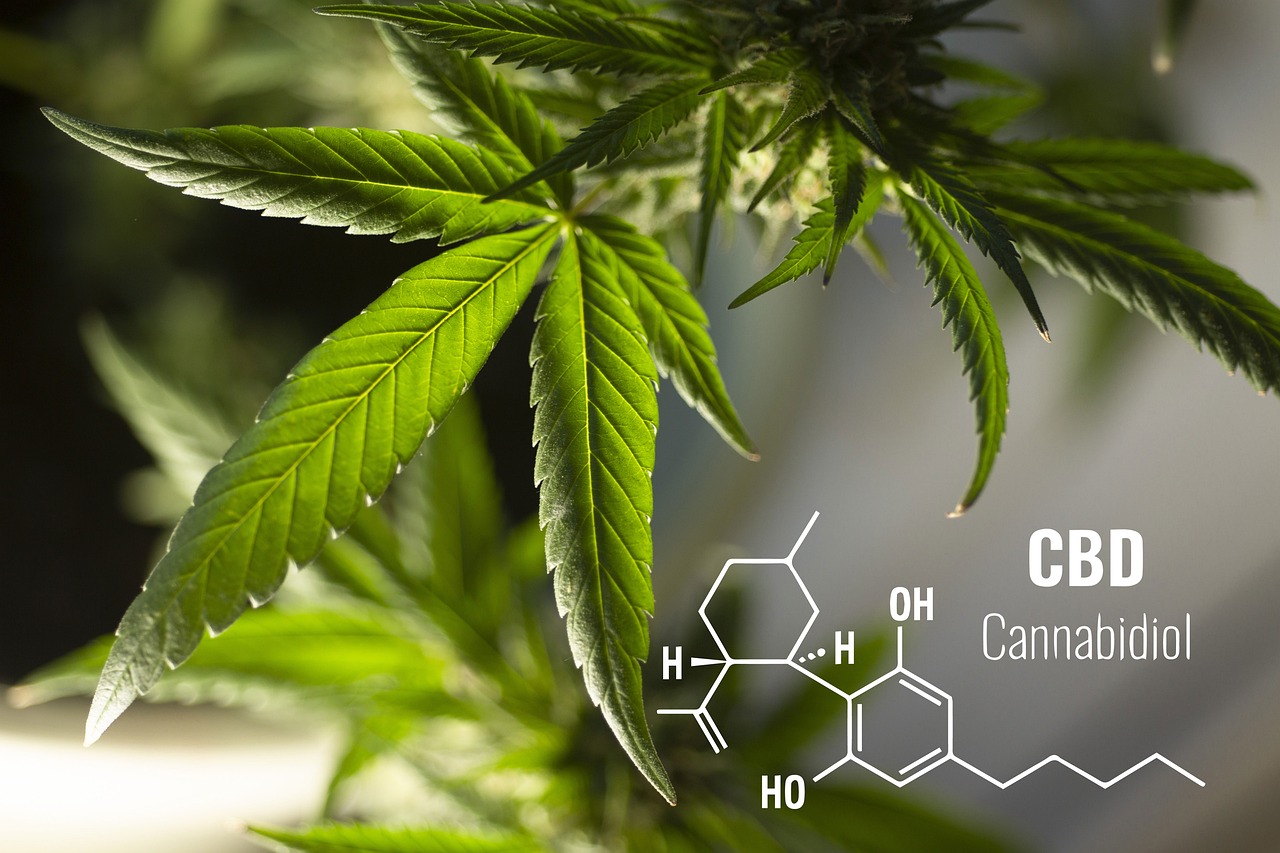
That’s why by taking CBD you get
- Muscle relaxation. US Academy of Sciences report states that taking CBD promotes relaxation of various muscle groups both skeletal and visceral muscles. Accordingly, medical use of CBD includes combatting muscle spasms and clamps. This CBD effect also explains why marijuana is so demanded by athletes.
- Anti-inflammatory effect. According to the same report, CBD prevents the development of myositis and inflammatory lesions of the skeletal muscles as well as it fights neurological inflammations. Already now in some countries, for example, in the USA, cannabidiols are widely used for the treatment of spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, Drave's syndrome and Crohn's disease.
- Pain relief. Reducing chronic pain is one of the main clinically approved prescriptions for the use of cannabis. For example, CBD is the most effective medicine in relieving migraine attacks. Also, due to the anti-inflammatory and relaxing properties, CBD effectively combats muscle and joint pain.
- Anxiety reduction. Some medical research suggests that CBD may increase the synaptic response of serotonin level. By nowadays the usage of CBD to treat dogs and cat with anxiety has already been proven, but there are not enough data for official CBD usage in a clinical practice for the human stress level reduction. However, in medical practice already now CBD is often prescribed for people with various types of anxiety, including post-traumatic stress syndrome.
- Changes in sleep phases. There is a lot of research on how weed affects sleep. One of the most interesting studies is a long-term project at the University of Palo Alto, which has shown that high doses of CBD reduce the time of REM sleep (the fastest and deepest phase), but at the same time prevent early awakenings and disruption of nighttime sleep. As a summary of a number of other studies, we can assume that CBD is effective in combating anxiety-related insomnia as well as REM-disorders, but exclusively at low doses and in the short consumption term. Long-term use of CBD has a negative impact on the quality of sleep, primarily on its REM-phase (where you dream). Therefore, heavy smokers almost never see dreams. Looking ahead, it should be mentioned that THC effects sleeping phases similar way to CBD but stronger due to THC incitant properties.
- Slowing down cancerous processes. A number of studies show that cannabis helps to fight against cancer. If we talk only about CBD, on the one hand, it prevents or slows down the dividing of cancer cells, on the other hand, cannabidiols prevent the growth of blood vessels into the tumor, cutting off access of the disease to the body's resources. Nowadays, the anti-cancer properties of cannabis are one of the most promising research areas of marijuana medical usage.
CBD has no proven harmful effect on the human body, and it does not cause chemical dependency. However, be aware that CBD can cause diarrhea (due to muscle relaxation), as well as appetite suppression and, as a result, weight loss. At high doses, as we wrote above, problems with sleep phases are likely. With frequent use, CBD causes a psychological addiction similar to the addiction to caffeine or sugar, for example.
How does THC effect on human body?
THD (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the main psychoactive compound of cannabis, which primarily affects the human brain and nervous system. It is THD that is responsible for drug intoxication by smoking weed. Psychoactive effects of THC are associated with the activation of cannabinoid receptors in the cells of the central nervous system and the brain. Primarily it’s about those CNS and brain sections that are responsible for coordination, concentration, pleasure and a sense of time. Therefore, euphoria, hallucinations, inhibition of reactions, reduced sensitivity to pain and lack of coordination are common consequences of smoking weed.

Moreover, by taking THD you get
- Increase in appetite. Scientists explain feelings of hunger after consuming cannabis in two ways. Firstly, beta-endorphin and insulin, produced in the body by stimulating CNS receptors, increases appetite. Secondly, part of the stimulated receptors (CB1) is concentrated in the olfactory bulbs, their stimulation enhances the sense of smell. These properties are already quite widely used in medicine to combat nausea and weight loss for AIDS patients, for cancer patients during chemotherapy, and also to combat anorexia. By the way, oral use of cannabis has a stronger effect on appetite than smoking and vaporization.
- Anti-inflammatory effect on brain cells. In 2016, Salk Institute presented data on the possible neuroprotective effects of THC. According to the study, THC prevents the accumulation of an abnormal beta-amyloid proteins that are associated with the development of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
- Reducing the number of active brain cells, but increasing the number of neural connections between them. Another study concluded that regular use of high-THC cannabis, especially during adolescence, reduces the size of the orbitofrontal cortex (brain zone associated with emotion regulation, balance, and motivation), but increased the number of connections between different active brain cells.
- Decrease blood circulation in the brain. The American Academy of Neurology states that marijuana use affects blood flow in the brain even after abstinence.
- Fewer sperm production. Taking THC could contribute to decreased production of men's semen. However, long-term research shows that cannabis use is not associated with clinically significant deleterious effects on male sexual parameters in this cohort.
You also should know that CBD and THC can enhance or vice versa suppress each other's properties, depending on their ratio. Moreover, besides CBD and THC, marijuana contains more than 60 other active chemical compounds. The diversity and ambiguity of cannabis effects is partly explained by the different ratios of these active components. In addition, the initial state of health and the individual characteristics of each organism play an important role.
The way you consume cannabis also matters a lot. For example, although CBD has properties to inhibit the growth of tumors, the smoke we inhale while smoking marijuana has an opposite effect, and it is carcinogenic. The safest way of the medical marijuana use is vaporizing. Moreover, it should be borne in mind that the chemical reactions in the body, for example, when smoking or eating cannabis, are different. This is a topic for our next article.